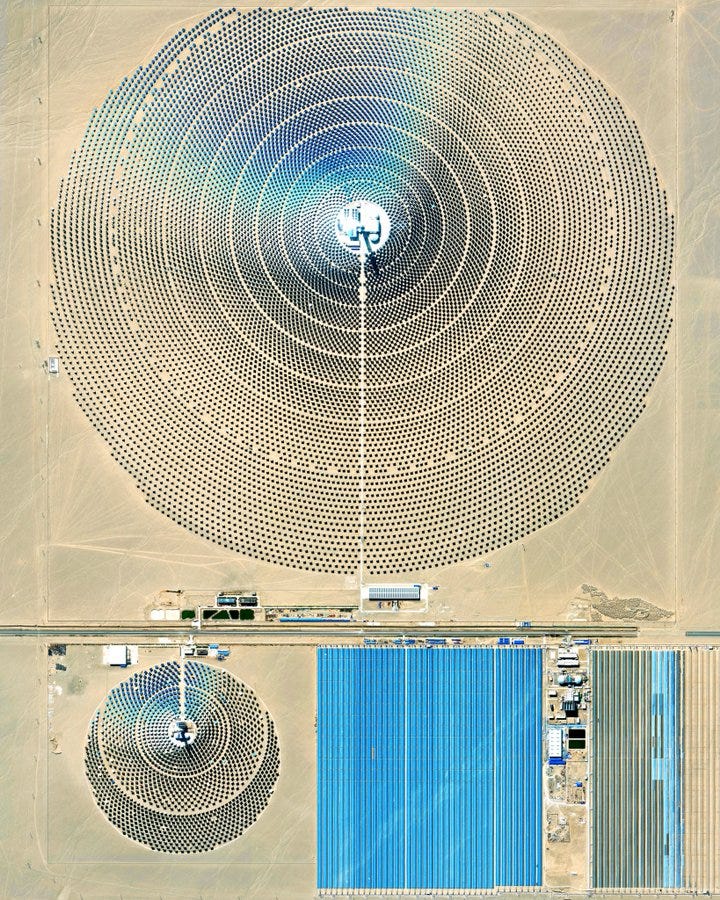
Concentrated solar power station (CSP, also known as concentrated solar thermal) near Dunhuang, China.
These plants use mirrors to focus the sun’s rays on molten salt (heated to about 400-500 degrees Celsius) flowing through a central tower, which circulates to storage tanks and is used to produce steam and generate electricity.
The larger circular array seen here is 2.7km wide, contains 12,000 mirrors and can displace 350,000 tonnes of carbon dioxide emissions annually. The station produces 100-megawatt solar thermal generating station capable of running around-the-clock, 365-days-a-year connected to the Northwest China regional power grid.
Another CSP technology is parabolic trough collectors, whose target is to concentrate solar beams towards a receiver tube (as opposed to the tower) located in the collectors' focus. The heat transfer fluid flows through the receiver tube.
We have been working on a few parabolic through collector plants in Africa. Using our hot tapping services, we have repaired the lines and isolated valves, allowing the plant to keep operating while repairs are made—because cooling down 400-degree molten salt is a problem!